A PROJECT REPORT ON “CUSTOMER SATISFACTION TOWARDS RELIANCE MUTUAL FUNDS- SHIMLA”
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
To carry out
this research work I have got help from my parents who have given full support to carry
out this research
work
It is my
privilege to express my indebtedness to respected teachers, parents, and friends without that help, this project
could not have been completed. Their able guidance, encouragement, and valuable
suggestions led my way pass easily
through a most difficult period
of the project.
Further, I would like to thank my guide Mrs./Mr.
for his guidance & concern, without which it would not have
been possible for me to complete this project.
I am highly indebted to the members of the faculty for the constant encouragement, valuable suggestion & requisite information & documents that were valuable for the completion of the project.
Date……….
DECLARATION
I hereby, . ......declare that I have done the training report on the topic “THE STUDY OF CUSTOMER
SATISFACTION TOWARDS RELIANCE
MUTUAL FUNDS
AT SHIMLA” is submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTERS IN BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION in HIMACHAL PRADESH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY. It is declared that it has an original piece of work& is worthy of the consideration for the degree of MBA.
~ Index |~
|
SNO |
TITLE |
PAGE NO |
|
CHAPTER-1 |
||
|
1.1 |
Industry profile |
7 |
|
1.2 |
Company profile |
10 |
|
1.3 |
History of reliance on the company |
11 |
|
1.4 |
About reliance mutual fund |
12 |
|
1.5 |
Vision and mission statement |
13 |
|
1.6 |
Reliance vision fund |
14 |
|
1.7 |
Organizational hierarchy |
16 |
|
1.8 |
Organizational structure |
18 |
|
1.9 |
Product profile |
19 |
|
1.10 |
Reliance media
& entertainment fund |
23 |
|
1.11 |
Functional departments |
24 |
|
1.12 |
Functions of the finance department |
24 |
|
1.13 |
Job description of people in the finance department |
25 |
|
1.14 |
Administrative officer (finance) |
25 |
|
1.15 |
Sales department |
27 |
|
1.16 |
Marketing activities in reliance on mutual fund |
28 |
|
1.17 |
HR Department |
30 |
|
1.18 |
HR structure |
31 |
|
CHAPTER-2 |
||
|
2.1 |
Research
methodology |
34 |
|
2.2 |
Need for the
study |
34 |
|
2.3 |
Data collection |
35 |
|
2.4 |
Importance of this study |
36 |
|
CHAPTER-3 |
||
|
3.1 |
Data analysis and interpretation |
38 |
|
3.2. |
Classification of respondents
on the basis of awareness |
39 |
|
3.3 |
Classification of respondents
on the basis of highly-volatile market |
40 |
|
3.4. |
Classification of respondents
on the basis of satisfaction with the different |
41 |
|
3.5. |
Classification of respondents on the basis of investing money |
42 |
|
3.6. |
Classification of respondents on the
basis of ever |
43 |
|
3.7. |
If yes, in which type of funds of mutual fund do you want to invest |
44 |
|
3.8. |
Which are the primary source of your knowledge about mutual funds |
45 |
|
3.9. |
Classification of respondents
on the basis of how to do
you |
46 |
|
3.10. |
Classification of respondents on the
basis of when you |
47 |
|
3.11 |
Classification of respondents on the
basis of which mutual funds |
48 |
|
CHAPTER-4 |
||
|
4.1 |
Findings |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
Conclusion |
51 |
|
4.3 |
Suggestions |
52 |
|
BIBLIOGRAPHY |
||
|
ANNEXURE |
||
|
QUESTIONNAIRE |
||
1.1 INDUSTRY PROFILE Introduction
A mutual represents a vehicle for collective investment.
Till 1986, the Unit Trust of India was the
only mutual fund in India. Since then public sector banks and insurance
companies have been allowed to set up
subsidiaries to undertake mutual fund business. So, State Bank of India, Canara Bank, LIC, GIC, and a few
other public sector banks entered the mutual fund industry.
In 1992, the mutual fund industry was opened to the private
sector, and a number of private sector
mutual funds such as Birla Mutual
Fund, DSP Merrill Lynch Mutual Fund, Kotak Mahindra
Mutual Fund, Morgan Stanley Mutual Fund, Tata Mutual Fund, Prudential ICICI Mutual Fund, Reliance Mutual Fund,
Standard Chartered Mutual Fund, Templeton Mutual Fund, IDBI- Principal Mutual Fund have been set up. The process
of consolidation began in recent years.
At present, there are about 30 mutual funds managing
nearly 1000 schemes. While the mutual fund
industry in India has registered a healthy growth over the last 15 years, it is
still very small in relation to other
intermediaries like banks and insurance companies. Mutual funds are one of the best investments ever
created because they are very cost-efficient and very easy to invest in. by pooling money together
in a mutual fund, investors can purchase stocks or bonds with much lower trading costs than if they tried to do it
on their own. But the biggest advantage
of mutual funds is
diversification.
The mutual fund industry in India started in 1963 with
the formation of Unit Trust of India, at the
initiative of the Government of India and Reserve Bank of India. The history of
mutual funds in India can be broadly divided
into four distinct
phases
First Phase
- 1964-1987
Unit Trust of India (UTI) was established in 1963 by an
Act of Parliament. It was set up by the
Reserve Bank of India and functioned under the Regulatory and administrative
control of the Reserve Bank of India.
In 1978 UTI was de-linked from the RBI and the Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI) took over
the regulatory and administrative control in
place of RBI. The first scheme launched by UTI was Unit Scheme 1964. At
the end of 1988, UTIs had Rs. 6,700 crores of assets
under management.
Second Phase -
1987-1993 (Entry of Public Sector
Funds)
1987 marked the entry of non-UTI, public sector mutual
funds set up by public sector banks and
Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) and General Insurance Corporation of
India (GIC). SBI Mutual Fund was the first non-UTI Mutual Fund established in June 1987 followed
by
Can bank Mutual Fund (Dec 87), Punjab National Bank
Mutual Fund (Aug 89), Indian Bank Mutual Fund (Nov 89), Bank of India (Jun 90), Bank of Baroda Mutual Fund (Oct 92). LIC
established its mutual fund in June 1989 while GIC had
set up its mutual fund in December 1990.
At the end of 1993, the mutual fund industry had assets
under the management of Rs. 47,004 crores.
Third Phase -
1993-2003 (Entry of Private Sector
Funds)
With the entry of private sector funds in 1993, a new
era started in the Indian mutual fund industry,
giving the Indian investors a wider choice of fund families. Also, 1993 was the
year in which the first Mutual Fund
Regulations came into being, under which all mutual funds, except UTI, were to be registered and
governed. The erstwhile Kothari Pioneer (now merged with Franklin Templeton) was the first private
sector mutual fund registered in July 1993.
The 1993 SEBI (Mutual Fund) Regulations were substituted
by a more comprehensive and revised Mutual Fund Regulations in 1996. The industry
now functions under the SEBI (Mutual Fund) Regulations
1996.
The number of mutual fund houses went on increasing,
with many foreign mutual funds setting
up funds in India, and also the industry has witnessed several mergers and
acquisitions. As of the end of
January 2003, there were 33 mutual funds with total assets of Rs. 1, 21,805 crores. The Unit Trust of India with Rs.
44,541 crores of assets under management was way ahead of other mutual funds.
Fourth Phase -
since February 2003
In February 2003, following the repeal of the Unit Trust of India Act 1963 UTI was bifurcated into two separate entities. One
is the Specified Undertaking of the Unit Trust of India with assets under management of Rs. 29,835 crores as of
the end of January 2003, representing
broadly, the assets of the US 64 scheme, assured return, and certain other schemes. The Specified Undertaking of Unit Trust of
India, functions under an administrator and
under the rules framed by the Government of India and does not come under
the purview of the Mutual Fund Regulations.
The second is the UTI Mutual Fund, sponsored by SBI,
PNB, BOB, and LIC. It is registered with
SEBI and functions under the Mutual Fund Regulations. With the bifurcation of
the erstwhile UTI which had in March 2000 more than Rs. 76,000 crores of assets under management and with the setting up of a
UTI Mutual Fund, conforming to the SEBI Mutual
Fund Regulations, and with recent mergers taking place among different
private sector funds, the mutual
fund industry has entered its current phase of
consolidation and growth.
Structure of the Indian
mutual fund industry:
The Indian mutual fund industry is dominated by the Unit
Trust of India, which has a total corpus
of Rs700bn collected from more than 20 million
investors. The UTI has many funds/schemes
in all categories i.e. equity, balanced, income, etc. with some being open-ended and some being closed-ended. The
Unit Scheme 1964 commonly referred to as US 64, which is a balanced fund, is the biggest scheme with a corpus of
about Rs200bn. Most of its investors
believe that the UTI is government-owned and controlled, which, while legally incorrect, is true for all practical purposes.
The second-largest category of mutual funds is the ones floated by
nationalized banks. Can bank Asset Management
floated by Canara Bank and SBI Funds Management floated
by the State
Some of the AMCs operating currently are:
|
Name of the AMC |
Nature of ownership |
|
Alliance Capital Asset
Management (I) Private Limited |
Private foreign |
|
Birla Sun Life
Asset Management Company
Limited |
Private Indian |
|
Bank of Baroda
Asset Management Company
Limited |
Banks |
|
Bank of India
Asset Management Company
Limited |
Banks |
|
Can bank Investment Management Services Limited |
Banks |
|
CholamandalamCazenove Asset Management Company Limited |
Private foreign |
|
Dundee Asset Management Company Limited |
Private foreign |
|
DSP Merrill Lynch
Asset Management Company Limited |
Private foreign |
|
Escorts Asset Management Limited |
Private Indian |
|
First India Asset
Management Limited |
Private Indian |
|
GIC Asset
Management Company Limited |
Institutions |
|
IDBI Investment
Management Company Limited |
Institutions |
1.2
COMPANY PROFILE
Introduction
There are a lot of investment avenues available today in
the financial market for an investor with
an investable surplus. He can invest in bank deposits, corporate debentures, and bonds where there is low
risk but low return. He may invest in funds of the companies where the risk is high and the returns are also proportionately high. The
recent trends in the mutual fund market
have shown that an average retail investor always lost with periodic bearish
tends people began for opting for
portfolio managers with expertise. In mutual fund market would invest on their behalf. Thus we have wealth management services provided by many institutions. However, they prove to be
costly for small investors. These investors have found a good shelter with the mutual funds.
Like most developed and developing countries the mutual fund cult is catching on in India
the reason for its interesting occurrence are :
·
Mutual funds make it easy and less
costly for investors to satisfy their need for capital growth income.
· It brings the benefits of diversification and money management to the individual investor, providing an opportunity for financial success that was once available to only a select few.
1.3 History of Reliance Company
The Reliance group founded by Dhirubhai H. Ambani
(1932-2002) is India’s largest private-sector enterprise. He is credited to have brought about the equity cult in India in the
late seventies and is regarded as
an icon of enterprise in India. The Reliance group is a living testimony to his indomitable will, single-minded dedication, and unrelenting commitment to his goals.
The unit trust of India is the first mutual fund set up under
the separate Act UTI ACT in 1963 and started
its operations in 1964 with the issue of schemes US-641. In 1978 UTI was
delinked from RBI and the industrial
development bank of India (IDBI) took over the
regulatory and administrative control in place of RBI.
In the year 1987, public sector banks like the state bank of
India, Punjab national bank, Indian bank, bank of India, and bank of Baroda set up mutual funds.
Apart from the abovementioned banks' life insurance
corporations (LIC) and General Insurance Corporation have set up mutual funds. LIC established its mutual funds in june1989 while gig had set up its mutual funds in
December 1990. The mutual fund industry had assets under the management of RS 47,004 crore. With the entry of private
sector funds, a new era has started in the mutual
fund industry. e.g. Principal mutual fund.
1.4 About Reliance mutual funds
Reliance mutual funds are one of India’s leading
mutual funds with average assets under management
of Rs. 1,12,914 crores (April 14 – June 14 quarter ) and 52.69 Lakhs folios. (30thjune 2014).
Reliance mutual fund is a part of the reliance group one
of the fastest-growing mutual funds in India.
RMF offers investors a well-rounded portfolio of products to meet varying
investors' requirements and has
a presence in 179 cities across the country Reliance mutual funds constantly endeavor to launch innovative products and customer
service initiatives to increase
value to investors. Reliance capital asset management limited (RCAM) is the set manager
of the reliance mutual fund. RCAM is a subsidiary of reliance capital
limited (RCL).
Presently, RCL holds Up to 65.23% of its total issued and
paid-up equity share capital, and the balance
of its issued and paid-up equity share capital is held by other shareholders
which include Nippon life insurance
company (“NLI” ) holding 26% of RCAM’s total issued and paid-up equity share capital. NLI acquired the said 26% shareholding in RCAM on August 17, 2012.
Reliance capital ltd is one of India’s leading and fastest-growing private sector financial services companies and ranks among the top 3 private sector financial services and banking companies in terms of net worth. Reliance capital ltd has an interest in asset management, life and general insurance, private equity and proprietary investments, stockbroking, and other financial services.
|
Sponsor |
Reliance Capital Limited |
|
Trustee |
Reliance Capital Trustee co. Limited |
|
Investment manager |
Reliance Capital Asset
Management Limited |
|
Statutory details |
The sponsor, the trustee, and the investment manager are in corporate under the companies act 1956. |
1.5
Vision and mission statement
Vision statement
To be a globally respected wealth creator with an emphasis on customer care and a culture of good corporate governance.
Mission statement
To create and nurture a world-class high-performance environment aimed at delighting our customers.
Corporate Governance
Reliance capital asset management limited
has a vision of being a leading
player in the mutual fund business and has
achieved significant success and visibility in the market.
However an imperative part of growth and visibility is adherence to good conduct in the marketplace .at Reliance Capital Asset Management limited the implementation and observance of ethical processes and policies have helped us in standing up to the scrutiny of our domestic and international investors.
Key product and services
The aim of growth funds
is to provide capital
appreciation over the medium to
long term Such schemes
normally invest a major part of their corpus in equities such funds have comparatively high risks. These schemes
provide different options
to the investors like dividend option capital appreciation etc
and the investors may choose an option depending on their preferences.
Some of the key products of the reliance on mutual funds are as follows:-
1.6 Reliance vision fund:
the primary investment objective of this scheme is to achieve long-term growth of capital by investment
in equity and equity-related securities through a research-based investment approach.
Fund data type: Open-ended equity growth scheme. Date of allotment: 08-oct-1999
Inception date: 08-oct-1995 Minimum investment: Rs 1000
Net asset value as of 30th May 2014: Rs 340.53
Reliance growth fund: the primary investment objective of this scheme is to achieve long-term growth of capital by investment in equity and equity-related securities through a research-based investment approach.
Fund data type: Open-ended equity growth
scheme. Date of allotment: 08-oct-1995
Inception date: 08-oct-1995 Minimum investment: Rs 1000
Net asset value as of 30th May 214:Rs 612.67
Reliance small cap fund: the primary
investment objective of the scheme is to generate long-term capital appreciation by investing predominantly in equity and equity-related
instruments of small-cap companies
and the secondary objective is to generate consistent returns by investing
in debt and money market securities.
Fund data type: An open-ended equity
scheme. Date of allotment: 16 Sep 2010
Inception date: 21 Sep 2010 Minimum investment: Rs 5000
Net asset value as of 30th may 2014: Rs 16.43
Reliance equity opportunities fund:
the primary investment objective of the scheme is to generate long term capital appreciation and provide long term growth opportunities by investing
in a portfolio constituted of equity securities and equity related securities
and the secondary objective is to
generate consistent returns by investing in debt and money market securities.
Fund data type: Open-ended diversified equity scheme
Date of allotment: 28 march 205
Inception date: 30 march 2005
Minimum investment: 5000
Net asset value as of 30th May 2014: Rs 56.40
Reliance on regular saving fund - debt option: the primary investment objective is to generate optimal returns consistent with a moderate
level of risk. The income may be complemented by the capital appreciation of the portfolio. Accordingly, investments
shall predominantly be made in debt and money market instruments.
Fund data type:
open ended open-ended scheme Date of allotment: 08 June 2005
Inception date: 09 June 2005 Minimum investment: Rs 500
Net asset value as of 30th May 2014: Rs 17.49.
Reliance mutual funds in Bangalore have three functional units, they are following:
· Financial functional unit
· Marketing functional unit.
· Operational functional unit.
1.1
ORGANISATIONAL HIERARCHY
Reliance follows the functional structure where the company is divided into segments/separate units based on the functions or roles such as human resources, sales and distribution, and operations. All the similar actives of the company are put into different departments and each of the departments is headed by the department head and these departmental heads have authority chief directly in case of any failure or loss. The functional structure offers a number of potential advantages as well as disadvantages.
Advantages:-
· Specializations / favourable impact on employees:
An advantage of a functional organisational structure is that it offers a high level of specialization. Each unit operates as a
type of self-contained mini-company, changed with carrying out its specific role. Employees typically start their
careers in an entry-level position within
the function and develop specialized knowledge as they move up within the
hierarchy. They become experts within
their functional area, and the unit and company benefit from their expertise
and experience over time.
·
Efficiency and productivity / favourable impact on employees:
A worker who is an expert in his functional area can
perform tasks with a high level of speed and
efficiency, which enhances productivity. Workers who know their jobs well can
proceed with confidence and with a
minimum amount of mistakes. Because the career
paths within the functional unit are
clear, the employees may be highly motivated to advance their careers by reaching the next rung on the ladder, which may
also make them more productive.
Disadvantages:-
· Lack of teamwork:
While specialized units within the functional structure
often perform with a high level of efficiency,
they may have different working well with others units. If a project calls for several units to work together, units may
become territorial and unwilling to cooperate with each other. In essence, each unit may act in what it perceives
to be its own best interest instead
of those of the organization as a whole. Infighting may cause projects to fall
behind schedule.
·
Difficult management control:
Another potential disadvantage of the functional
organization structure is that it can pose a
challenge for top management to maintain control
as the organization expands. As organizations get larger and top management needs to delegate
more decision-making responsibilities in each functional area, the degree of autonomy may also increase, making coordination of activities more difficult.
1.8 ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
1.1 PRODUCT PROFILE
A. Equity Schemes:-
a. Reliance Equity Fund:
(An open-ended diversified Equity Scheme) The primary
investment objective of the scheme is
to seek to generate capital
appreciation & provide long-term
growth opportunities by investing in a portfolio constituted of
equity & equity-related securities of top 100 companies by market capitalization & of
companies that are available in the derivatives segment from time to time and the secondary objective
is to generate consistent returns by investing in debt and money market
securities.
b. Reliance Tax Saver (ELSS) Fund:
(An Open-ended Equity Linked Savings Scheme.) The
primary objective of the scheme is to generate
long-term capital appreciation from a portfolio that is invested predominantly
in equity and equity-related instruments.
c. Reliance Equity Opportunities Fund:
(An Open-Ended Diversified Equity Scheme) The primary investment objective of the scheme is to seek to generate capital appreciation & provide long-term growth opportunities by investing in a portfolio constituted of equity securities & equity-related securities and the secondary objective is to generate consistent returns by investing in debt and money market securities.
d. Reliance Vision Fund:
(An Open-ended Equity Growth Scheme.) The primary
investment objective of the Scheme is to
achieve long-term growth of capital by investment in equity and equity-related
securities through a research-based investment approach.
e. Reliance Growth Fund:
(An Open-ended Equity Growth Scheme.) The primary investment objective of the Scheme is to achieve long-term growth of capital by investment in equity and equity-related securities through a research-based investment approach.
f. Reliance Index Fund:
(An Open Ended Index-Linked Scheme.) The Investment
Objective under the Nifty Plan is to replicate
the composition of the Nifty, with a view to endeavor to generate returns,
which could approximately be the same as that of the Nifty. The Investment Objective
under the Sensex
a. Reliance NRI Equity Fund:
(An open-ended Diversified Equity Scheme.) The Primary investment objective of the scheme
is to generate optimal returns by investing in equity or equity related
instruments primarily drawn from the Companies in the BSE 200 Index.
B. Debt Schemes:
a. Reliance Monthly Income Plan:
(An Open Ended Fund Monthly Income is not assured &
is subject to the availability of distributable
surplus) The primary investment objective of the Scheme is to generate regular income in order to make regular dividend
payments to unitholders and the secondary
objective is the growth of capital. Primarily the investment shall be made
in debt and money market securities (i.e. 80%) with a small
exposure (i.e. up to 20%) in equity.
b. Reliance Gilt Securities Fund - Short
Term Gilt Plan & Long Term Gilt Plan:
Open-ended Government Securities Scheme) the primary objective of the Scheme is to generate optimal credit risk-free returns
by investing in a portfolio of securities issued and guaranteed by the Central Government and State Government
c. Reliance Income Fund:
(An Open-ended Income Scheme) The primary objective of
the scheme is to generate optimal returns
consistent with moderate levels of risk. This income may be complemented by the capital appreciation of the
portfolio. Accordingly, investments shall predominantly be made in Debt & Money Instruments.
d.
Reliance Medium Term Fund:
(An Open End Income Scheme with no assured returns.) The
primary investment objective of the
Scheme is to generate regular income in order to make regular dividend payments
to holders and unit holders and the secondary
objective is a growth of capital.
a. Reliance Short Term Fund:
(An Open End Income Scheme)
The primary investment objective
of the scheme is to generate stable returns for investors with
a short investment horizon by investing in Fixed Income Securities of short-term maturity.
a. Reliance Liquid Fund:
(Open-ended Liquid Scheme). The primary investment
objective of the Scheme is to generate optimal
returns consistent with moderate levels of risk and high liquidity. Accordingly, investments shall predominantly be made in Debt and Money Market
Instruments.
b. Reliance Fixed Term Scheme:
(Close-ended Income Scheme) The primary objective of the
Scheme is to seek to achieve regular
returns/growth of capital by investing in
a portfolio of fixed income securities normally
maturing in line with the time profile of the plan with the objective of
limiting interest rate volatility.
c.
Reliance Floating Rate Fund:
(An Open End Income Scheme) The primary objective of the
scheme is to generate regular income
through investment in a portfolio comprising substantially of Floating Rate
Debt Securities (including floating
rate securitized debt and Money Market Instruments and Fixed Rate Debt Instruments swapped for floating
rate returns). The scheme shall also invest in
fixed-rate debt Securities (including fixed-rate securitized debt, Money
Market Instruments and Floating
Rate Debt Instruments swapped
for fixed returns.
d. Reliance NRI Income
Fund:
(An Open-ended Income scheme) The primary investment objective of the Scheme is to generate optimal returns consistent with moderate levels of risk. This income may be complemented by the capital appreciation of the portfolio. Accordingly, investments shall predominantly be made in debt Instruments.
e. Fixed Maturity Fund - Series I: Reliance
(A Close Ended Income Scheme)The primary investment
objective of the Scheme is to seek to
achieve regular returns/growth of capital by investing in a portfolio of
fixed income securities normally
maturing in line with the time profile of the Plan with the objective of limiting
interest rate volatility.
f.
Reliance Fixed Maturity Fund -
Series II:
(A closed-ended Income Scheme) The primary investment
objective of the Scheme is to seek to
achieve growth of capital by investing in a portfolio of fixed income
securities normally maturing in line with the time profile of the respective plans.
g. RELIANCE REGULAR SAVINGS FUND:
(An Open-ended scheme)
The Investment Objectives:-
Debt Option: The primary investment objective of this plan is to generate optimal
returns consistent with a moderate level of risk. This income may be complemented by the capital appreciation of the portfolio. Accordingly, investments shall
predominantly be made in Debt
& Money Market
Instruments.
Equity Option: The primary investment objective is to seek capital appreciation and
or consistent returns by actively
investing in equity / equity-related securities.
Hybrid Option: The primary investment objective is to generate a consistent return by investing
a major portion in debt & money market securities and a small portion in equity & equity-related instruments.
Sector Specific Schemes
Sector Funds are specialty funds that invest in stocks
falling into a certain sector of the economy.
Here the portfolio is dispersed or spread across the stocks in that particular
sector. This type of scheme is ideal
for investors who have already made
up their minds to confine risk and return to a particular sector.
Reliance Banking Fund
Reliance Mutual Fund has an Open-Ended Banking Sector
Scheme which has the primary investment
objective to generate continuous returns by actively investing in equity/equity-related or fixed income securities
of banks.
Reliance Diversified Power Sector
Fund
Reliance Diversified Power Sector Scheme is an Open-ended Power Sector Scheme. The primary investment objective of the Scheme is to seek to generate consistent returns by actively investing in equity / equity-related or fixed income securities of Power and other associated companies.
Reliance Pharma Fund
Reliance Pharma Fund is an Open-ended Pharma Sector
Scheme. The primary investment objective
of the Scheme is to generate
consistent returns by investing in
equity-related or fixed-income securities of Pharma and other associated companies.
1.1
Reliance Media & Entertainment Fund
Reliance Media & Entertainment Fund is an Open-ended
Media & Entertainment sector scheme.
The primary investment objective of the Scheme is to generate consistent
returns by investing in equity /
equity-related or fixed income securities of media & entertainment and other associated companies.
1.2
Functional departments.
Functional areas of the Reliance
Industry Ltd. Mutual
fund Bangalore
1. FINANCING DEPARTMENT
2.
SALES DEPARTMENT
3. HUMAN RESOURCE DEPARTMENT
Finance department
Finance is the lifeblood of business. Finance is the
base of all corporate activities in the day-to-day world. Management of finance is broadly concerned with the acquisition and
use of funds by a business firm.
Reliance mutual fund has a very efficient Finance
Department headed by Manager Finance. All
the Finance Department staffs are professionals. The finance department consist of
a team of professionals headed by the Manager Finance, having sufficient industry
experience in the field of accounting, costing,
taxation, company law, and
financial management
OBJECTIVES OF THE FINANCE DEPARTMENT
1. To manage & account
for the financial
resource of the organization, forecast its requirement in the future
and plan accordingly, and check for deviation.
2. Report the financial performance of the organization, to comply with the government rules and regulations.
1.3
FUNCTIONS OF THE FINANCE DEPARTMENT
The main functions
of the finance department are defined as follows:-
1.
Recording of day-to-day business transactions.
2.
Receiving payments from customers and accounting for these funds.
3. Preparations of sales budgets
and revenue budgets and expenditure budgets on a quarterly basis.
4.
Preparations of fund flow and cash flow statement for every month.
5.
Preparing and filing quarterly and final income tax returns.
6.
Preparations and implementation of cost reduction
and cost control methods.
7.
Conduct and coordinate internal and stationary audits.
8. Perpetual stock verification and asset evaluation.
1.4
JOB DESCRIPTION OF PEOPLE
IN FINANCE DEPARTMENT Responsibility of people in the finance department
Establishing and controlling the financial systems
and administrative services
of the organization, and providing
financial information to the Board of Directors.
MANAGER (FINANCE)
Main duties
·
Directing the establishment of financial/accounting principles, procedures, and practices in line with legal and corporate requirements.
·
Ensuring accurate and timely
financial reports and forecasts for the whole
organization so as to provide
a clear insight into its financial condition.
·
Ensuring that the profits of the organization are protected through
the establishment of effective
financial controls; implementing and maintaining appropriate management accounting and reporting systems, budgetary controls,
and expenditure procedures.
1.5
ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICER
(FINANCE) Main duties
·
Providing accurate and timely
financial reports and forecasts and general accounting and administrative services.
· Ensuring effective costing and contribution analysis.
· Implementing policies
to ensure the security of funds and assets.
CASHIER
Main duties
· Maintain an awareness of all promotions and advertisements.
·
Accurately and efficiently ring
on registers and accurately maintain all cash and media at the registers.
· Communicate customer requests to top management.
INTERNAL AUDIT
The audit of all branch
office departments of the corporation is completed every year financial year. In keeping with the practice of improving our
systems and procedures through the use
of IT as a tool, audit packages are being used so that our auditors are able to
carry out the audit in a Front End Applications package environment.
INSPECTION
The inspection of all the branches of the corporation in
India is completed within the time schedule.
Implementation of inspection package in all our offices led to transparency by online report writing,
acceptance of compliance, and closure
process.
VIGILANCE
Special efforts were made to focus on the disposal of
vigilance cases pending for more than one year.
Besides expediting the disposal of vigilance cases, emphasis is also laid on
preventive vigilance through
the dissemination of information on areas susceptible to vigilance.
NOMINEE DIRECTORS
The corporation appoints nominee directors on the board
of the companies where it has a substantial stake by way of debt or
equity. Nominees are officials of the corporation who are in service or retired. Adequate systems
are in place to review and guide the nominee directors from time to time. Nominee directors provide feedback with
regard to operations problems, prospects, corporate governance standards, etc.
RISK MANAGEMENT
The corporation is the largest institutional investor in the
financial market and its staggering fund size
which is placed in varying asset classes is exposed to various financial risks.
To mitigate the investment risks
arising out of market risk, credit risk, interest rate risk and other risks inherent in the financial market, a
distinct full-fledged Risk management structure has been created in the corporation.
BOARD MEETINGS
Board meetings as per regulations are generally held
once in three months. In addition to policy matters,
the board provides
strategic direction for execution ensures
financial discipline and
accountability to the policyholders, and also ensures the interest of the policyholders and stakeholders.
1.6 Sales
Sales management is a business discipline that is
focused on the practical application of sales
techniques and the management of organizational sales operations. It is an
important business function as net
sales through the sale of products and services and resulting profit drive most commercial businesses. These are also typically
the goals and performance indicators of sales management. The art of meeting the sales targets
effectively through meticulous
planning and budgeting refers to sales management. Sales Management helps to extract the best out of employees and
achieve the sales goals of the organization in the most effective ways.
Process of Sales Management
· Sales Planning
·
Marketers must plan things
well in advance for the best results.
It is essential to have concrete
plans. Mere guess works
do not help in business.
·
Know the product well. Sales
professionals must know the benefits of the product for the consumers to believe them.
· Identify the target market.
·
Sales Planning makes the products available
to the end-users at the right
time and at the
right place.
·
Sales Planning helps marketers to analyze the customer demands
and respond efficiently to fluctuations in the market.
· Devise appropriate strategies to increase
the sales of the products.
Sales Reporting
· Sales strategies are implemented in this stage.
·
Check the effectiveness of the various
strategies. Find out whether they are bringing
the desired results or not.
·
Ask the sales team to submit
reports of what they have done throughout the week. The management must sit with the sales
team frequently to assess their performance and chalk out the future courses of action.
Sales Process
·
Sales process refers to various activities which help in the timely achievement of sales targets
for the successful functioning of an organization.
·
Sales Process includes various
strategies and techniques employed by an individual to achieve
sales goals within the stipulated time frame.
·
MANAGER (SALES)
The sales manager is the typical title of someone whose role
is sales management. The role typically involves
sales planning, human resources, talent development, leadership, and control of resources
such as organizational assets.
Main duties
· Manage and coordinate all marketing, advertising, and promotional staff
and activities
·
Conduct market research to determine
market requirements for existing and future products
· Analysis of customer research,
current market conditions, and competitor information
· Develop and implement marketing
plans and projects
for new and existing products.
1.7 MARKETING ACTIVITIES IN RELIANCE MUTUAL FUND PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
In a competitive market, there is a greater need to
provide insurance products that meet the needs
of customers RMF therefore a wide variety of products that fulfill the needs
of different segments of the society.
As of the end of the financial year 2009-10, the corporation had 54 plans available for sale.
FIELD PERSONNEL TRAINING (FPT)
The theme of FPT is professionalism. For this purpose,
training in a big way is conducted across all zones
using reputed International / National
Training Institutions.
BANKASSURANCE &
ALTERNATE CHANNELS
Bank assurance is the term used to describe the partnership or relationship between a bank and an insurance company whereby the insurance company uses the bank sales channel in order to sell insurance products.
DIRECT MARKETING
This vertical is started with the objective of “creating
new systems for business generation, sales
process monitoring, and business processing with a view to reach out to untapped markets and provide improved
buying experience to customers.”
In a short period, the channel has expanded and professionally trained
Direct Sales Executives (DSEs) to provide financial advice
to prospective customers.
The main focus of the channel was setting up systems and
processes. A state of art lead management
system has been established to provide easy access to prospective customers to reach out to LIC to buy a policy. Such leads are captured
through our website.
www.reliancemutualfund.com is passed on to well-trained DSEs on real-time basis who can contact
the customer instantly.
AGENTS
Most people have their first contact with an insurance
company through an insurance sales agent.
These workers help individuals, families, and businesses select insurance
policies that provide the best protection for their lives, health, and property. Insurance
sales agents are commonly
referred to as “producers”
in the insurance industry.
Agency Strength
The total number
of agents in our role is 140280 as of 31.03.2011 as against
134485 as of 31.03.2012.
a) Agents’ Club Membership In order to motivate and recognize high performers amongst
agents a premium
club called the Corporate Club. The
other 5 clubs were formed to recognize
agents, who perform
consistently year after year.
MEMBERS OF VARIOUS AGENTS CLUBS
|
Name of the Club |
|
Corporate |
|
Chairman |
|
Zonal Manager |
|
Divisional Manager |
|
Branch Manager |
|
Distinguished Agents |
a) Career
Agents Scheme
The corporation has a scheme of Urban Career Agents and Rural Career
Agents to promote the cause of professionalizing
the agency force. They are given Stipends at the
start of their career to enable them to settle down in the profession.
a)
Chief mutual fund Advisor
Scheme
The corporation introduced the above scheme with the
objective of increasing its market presence through more agents by utilizing the capabilities of existing high-performing agents for organizational growth.
b)
Authorised Agents
In tune with the increasing customer expectation j select agents collect the renewal premium through “Premium Points”.
1.8
HR DEPARTMENT
For any business to run one needs four M’s namely Man,
Money, Machine, and Material. Managing
other three resources other than men,
are easy to handle. Men are very difficult to
handle because no two human beings are similar in all ways. Human beings
can think, feel and give responses.
Handling humans is more important for any business because human beings have crucial potential that may be very
profitable for the business. And this potential can be developed to an unlimited extent if they are
provided with the proper environment. So the function
of managing men is as important as the finance or marketing function
in any business.
HRM refers to practices and policies framed
for the management of human resources in an
organization, including Recruiting, screening, rewarding, and appraising. “Human
resources have at least two meanings depending on context. The original
usage derives from political economy and economics, where it was traditionally called
lab our, one of three factors of production.
The more common usage within corporations and businesses refers to the
individuals within the firm, and to
the portion of the firm's organization that deals with hiring, firing,
training, and other personnel issues.
This article addresses both definitions.
1.9 HR STRUCTURE CORPORATE HR:
Activities taken up by Corporate
HR are:
· Policymaking
· Implementing suggestions - HEWITT CONSULTANT
· Strategic planning.
ENTITY HR:
· Activities taken
up by Entity HR are :
· Execution of policies and practices
· Targets for recruitment of Circle HR.
PRESIDENT HR CORPORATE HR ENTITY HR CIRCLE HR CEO
CIRCLE HR:
Activities taken up by Circle HR are:-
· Recruitment
· Appointment
· Training
· Payroll
· Employees issues
HR FUNCTIONS
· Talent
acquisition
· Talent development
· Performance management system
· Training
· Carrier planning
· Suggestion planninh
TALENT MANAGEMENT
Operation HR RECRUITMENT PROCESS
STEP 1: MANPOWER PLANNING
AOP (Annual Operating Plan), this process is taken up
every year. It is taken up at Personal Level and Entity Level. Several points like
Revenue generation, Acquisition number, etc.
STEP 2: SOURCING ACTIVITY
There are three types of sourcing done at Reliance.
After candidates are chosen then the same is sent to the department head where the vacancy arises. The department
head will then shortlist the same and they ask the HR department to fix
an interview with the selected
candidates. There is two types of interview which is taken up at Reliance,
firstly the Functional interview, and then the Functional Head and HR Head takes the interview.
INTERNAL source
Employee Reference
Re-employment of former
employee EXTERNAL SOUCING
Placement Consultant – Ruchika,
the Age, the Avenue. Job Portals - Monster, NAUKRI.
Campus Recruitment
STEP 3: APPROVAL.
The HR executives will negotiate the CTC with the candidate. Then after it is
sent to ECRC
Then the same is sent to CRL
The same is then sent to Management for SAP Applicant Code.
CHAPTER-2
OBJECTIVES, SCOPE, AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
2.1 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research Methodology is a way to systematically solve the
research problems. It involves adopting
various methods and techniques which are best suited for the research and study
of the problem, for investigation and
analysis of the problem starts with data collection from various sources i.e. primary and secondary
sources, data analysis and interpretation, and finally the finding. The research methodology comprises two
Research + Methodology.
Research methodology is a way to solve the problem scientifically and systematically. It basically includes the selection of various methods and techniques in the research conducted.
2.2 NEED FOR THE STUDY
The main
purpose of doing this project was to
know about mutual funds and customer satisfaction This also helps to know in
detail about various mutual fund
schemes and also the performance of various mutual fund schemes
It also helps in
understanding how a fund is being designed
It also helps in
understanding whether a Sales manager's
decisions and strategy
also affect the customer satisfaction
RESEARCH OBJECTIVES:
· The study level of satisfaction of customers towards
Reliance Mutual Fund.
·
To find the customer’s preference
for various options available in Reliance Mutual Fund.
· To know the kind of benefits people expected
from Reliance Mutual Fund.
SCOPE OF THE STUDY
The study urges to know the customer
satisfaction, current market trend and performance and also to improve the existing services and to add on anything
if required the study also helps to understand risk and hence informed about investment decisions
for better performance of the company.
Research Design
The research design is a pattern or an outline of a research project.
It is a statement of only the essence of a study that provides
the basic guidelines for the detail of the project.
Research design stands for advance
planning of the method to be used in their analysis,
keeping in view the objective of the research and availability of staff, time and
money.
Sample Technique
The sampling procedure refers to the technique which is used in selecting the items for the sample infect; this technique of procedure stands for the sample design itself. The sampling procedure for the study is convenient sampling.
2.3 DATA COLLECTION
There are several ways of collecting the appropriate data which differ considering in the context of money, costs, time, and other resources data can be collected through different sources.
Primary data
Primary data was collected through a survey method by distributing questionnaires to the different customers of reliance on mutual funds in the Bangalore branch
Secondary data
The secondary data collection includes a collection of data through sources like
1. Fund facts sheets of different AMC that are considered for the analysis
purpose
2. The NAVs
are taken from AMFI & websites of the AMC under consideration
3. From record,
report, magazine, and websites or RMF.
2.4 IMPORTANCE OF THIS STUDY
Ø Every
person who has no knowledge about investment can easily invest in mutual funds
Ø One of the mode of investing
in mutual funds
is SIP’s systematic investment plan is less risky to invest and every investor wants to invest on less price.
Ø
Mutual fund is totally dependent
on NAV [net asset value]
Ø Comparatively investors
have limited risk since the
investments are managed
by the highly experienced and qualified fund manager
Ø The
primary investment objective of the Scheme is to achieve long-term growth of capital
by investing in equity and equity-related securities through a research-based investment approach. However,
there can be no assurance
that the investment
the objective of the Scheme will be realized,
as actual market movements may be at variance
with anticipated trends.
Ø This study helps to know about the level of customers satisfaction and whether distributors are happy with the performance of Reliance Mutual Funds
LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDYØ
![]() ØTime constraints: due to
less availability of time it may be possible that all the related aspects
May not be covered in the project.
ØTime constraints: due to
less availability of time it may be possible that all the related aspects
May not be covered in the project.
ØAnalysis is done with the limited availability of the data
CHAPTER-3
DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
3.1 DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE BASIS OF
AGE
Table no 3.1
|
Serial no. |
Age group |
No. of respondent |
percentage |
|
1. |
18-25 |
22 |
22 |
|
2. |
25-23 |
32 |
32 |
|
3. |
35-45 |
28 |
28 |
|
4. |
45 & above |
15 |
18 |
|
|
Total |
100 |
100 |
Source: Data collected through questionnaire method
Fig 3.1
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents 32 percent are in the age group of 25-35 years.
3.2. CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE BASIS OF
AWARENESS
|
Sr. No |
Response |
No.of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Yes |
30 |
60 |
|
2 |
No |
20 |
40 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |

INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e. 60% of respondents are aware of reliance on mutual funds.
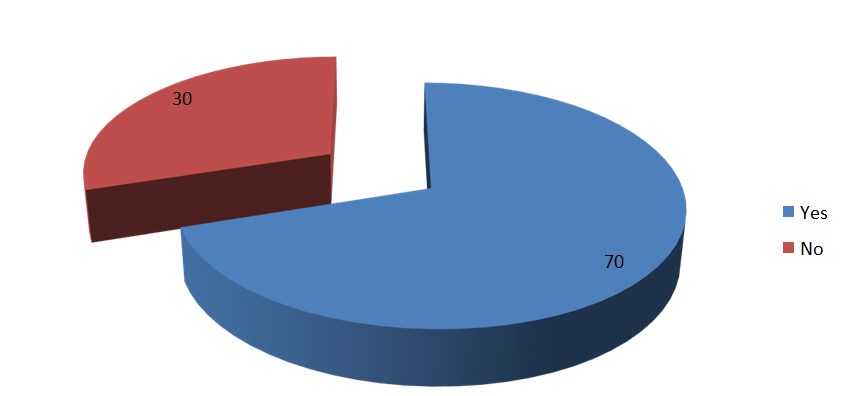
3.3. CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE
BASIS OF HIGHLY VOLATILE MARKET, DO YOU THINK MUTUAL
FUNDS ARE THE DESTINATION FOR INVESTMENT?
|
Sr.NO |
Response |
No. Of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Yes |
35 |
70 |
|
2 |
No |
15 |
30 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e. 70% of respondents think mutual funds are the destination for investment.
3.4. CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENT OF THE BASIS OF Satisfy With The Different Types Of Products And Services Provided By Reliance Mutual Funds?
|
Sr. No |
Response |
No. of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Yes |
40 |
80 |
|
2 |
No |
10 |
20 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |

 INTERPRETATION
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e. 80% of respondents satisfy
with the different types of
products and services.
3.5. CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE
BASIS OF INVESTING MONEY, WHICH FACTORS DO YOU PREFER MOST?
|
Sr. No. |
Response |
No. of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Liquidity |
15 |
30 |
|
2 |
Low risk |
16 |
32 |
|
3 |
High return |
9 |
18 |
|
4 |
Company reputation |
10 |
20 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e. 32% of respondents prefer the liquidity factor.
3.6.
CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE BASIS OF EVER INVESTED
IN MUTUAL FUNDS?
|
Sr. No. |
Response |
No. of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Yes |
30 |
60 |
|
2 |
No |
20 |
40 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
|
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is
concluded that the majority of respondents i.e. 60% respondents invested in mutual
funds. |
3.7. If yes, which type of
funds of mutual
funds do you want to invest
|
Sr. No. |
Response |
No. of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Fixed deposit |
16 |
32 |
|
2 |
Mutual funds |
4 |
8 |
|
3 |
Equities |
10 |
20 |
|
4 |
Others |
20 |
40 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e. 40% of respondents invest
in other types of
investments.
3.8. What ARE THE PRIMARY SOURCES OF YOUR KNOWLEDGE ABOUT MUTUAL FUNDS AS AN INVESTMENT
OPTION?
Corresponding to your
choice how would you
rate their influence on your final mutual funds' purchase
decisions? 1 is the lowest and 5is the highest
rating
|
Sr. No. |
Sources |
No.of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Television |
30 |
60 |
|
2 |
Internet |
6 |
12 |
|
3 |
Newspaper |
4 |
8 |
|
4 |
Friends |
5 |
10 |
|
5 |
Sales |
5 |
10 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e60% of respondents influence by television.
3.9. CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE BASIS OF HOW YOU RATE
THE RISK ASSOCIATED WITH MUTUAL FRIENDS?
|
Sr. No. |
Response |
No. of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Low |
10 |
20 |
|
2 |
High |
30 |
60 |
|
3 |
Moderate |
10 |
20 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e60%
of respondents associated with high risk in mutual funds.
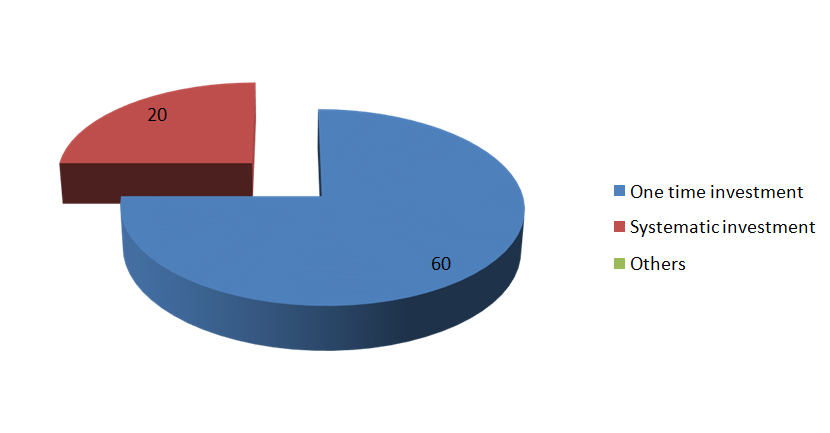
3.10. CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE
BASIS OF WHEN YOU INVEST IN MUTUAL FUNDS WHICH MODE OF INVESTMENT WILL YOU PREFER?
|
Sr. No. |
Response |
No. of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
One time investment |
30 |
60 |
|
2 |
Systematic investment |
10 |
20 |
|
3 |
Others |
10 |
20 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority of respondents i.e60% of respondents invest in one time in investment.
3.11. CLASSIFICATION OF RESPONDENTS ON THE BASIS OF IN WHICH MUTUAL
FUNDS YOU HAVE INVESTED?
|
Sr. No. |
Response |
No. of respondents |
Percentage |
|
1 |
SBIMF |
20 |
40 |
|
2 |
UTI |
10 |
20 |
|
3 |
RELIANCE |
10 |
20 |
|
4 |
HDFC |
10 |
20 |
|
|
Total |
50 |
100 |
INTERPRETATION
Hence it is concluded that the majority
of respondents i.e40% of respondent invest in SBIMF.
CHAPTER-4
FINDINGS, CONCLUSION & SUGGESTIONS
4.1 FINDINGS
67% of the respondent's rate performance of RMF is Very
Good, 27% rate excellent, and 6% rate Good . The majority of the respondents rate the performance of RMF as very good. (Table no. 2)
1. According
to the analysis, 57% of the respondents are satisfied by services provided by RMF,23% are neither satisfied nor
dissatisfied, 17% very satisfied, and 3% are
dissatisfied. The majority of the
respondents rate the services provided
by RMF as Good
(Table no. 3)
2. All the respondents tell Yes that RMF has a good impact as compared to other AMC in MF industry.
(Table no.5)
.4.87% of the respondents tell that RMF is very helpful
in analysing & making right choice of investments
to the investors, 13% tell To some extent. Majority of the respondents tell Yes RMF is very helpful in analysing &
making right choice of investments to the investors. (Table no. 6)
5. 73%
of the respondents feel that while taking a investment decision Performance
matters a lot, and 23% Consistency is
considered Majority of the respondents feel that while taking a decision
Performance matters a lot.
6.According to the rating, 43% of the respondents rate the equity performance of RMF in long run is Excellent, 40% rate it Very Good, and 17% rate it as Good.43% of the respondents rate the equity performance of RMF in long run is Excellent (Table no. 8)
4.2
CONCLUSION
The research shows that Equity Funds are performing well, but the investments from investors are less
in equity funds, because
of unawareness about mutual funds.
Therefore company has to take some steps to make aware
people of Mutual Funds, through advertisements
in Newspaper, Magazine, Commercial advertisement, distributing leaflets, Television, Radios. And I came for following conclusion
:
·
All the workers and staff work together to increase the organization’s profit
and thereby to increase its growth, each department works without any failures.
· Very less people
knows about the service of Reliance.
·
Managing complex business processes is one of the important
management challenges of this new century. Moreover,
globalization and technological advancement are driving changes in all sectors. In reliance organisational
structure and management style are playing an important role in Information Technology Management.
·
Structure is influenced by the external
environment in which the business operates
as well as its culture and the nature of the work
and activities it undertakes.
· The structure can have both a positive
and negative impact on a business.
·
Having the right structure
allows a business
to respond and adapt to changes
in the market quickly.
· The company
needs to adopt new strategy’s to have an efficient departments
. The
organization is following highly appreciable managerial practices, which made
it possible to the organizational
goals more easily. The HR policies set by the company are remarkable. Satisfied workers are
considered to be the assets of the organization and they are motivated enough to perform well. The
infrastructure facilities are very much impressive. There is a high rate of capacity
utilization. Quality management system is also remarkable.
·
By this study, I was able to
understand how the various functional departments of an organization co-ordinate and work towards achieving the
organizational goals in an effective
and efficient manner. I am sure that
my study at Reliance capital asset management was a success
and hope that it will be an asset for my future.
4.3
SUGGESTIONS
The awareness level of investors is low who are interested in dealing in mutual fund:
· Most of investors are totally unaware about this investment.
· Very less people
knows about the service of Reliance.
· Past image of mutual fund is not good.
·
Reliance can promote the investors by advertising, hording,
and by interviews to invest
in this fund.
·
Most of the investors want to
invest in public co.’s fund just because of safety purpose.
· Most of the investors
want to safer side in investment.
· Most of the investors want to invest in debt funds because those are the risk free funds; it gives the interest on investment.
·
Most of the investors don’t know
about the mutual funds so they want advisory
services from reliance which could provide
them whole information about the market
situation of mutual
fund.
ANNEXURE
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Book:
Ø Research Methodology Methods & Techniques by C R Kothari
Ø Philip Kotler, Gary Armstrong; “Principle of Marketing” Prentice-Hall of India 10th Edition
·
Reliance mutual fund Brochures and Manuals.
· Websites.
·
www.relianceimutualfund.com
·
www.amfi.com
QUESTIONNAIRE
DEAR SIR/MADAM,
I am...........student of MBA semester at..........., I am doing project on “CUSTOMER SATISFACTION TOWARDS RELIANCE MUTUAL FUNDS AT SHIMLA,”. Please give your precious time for filling this detail.
PERSONAL DETAILS:
SECTION – A
a) Name b) Gender
c)Address d) Profession
SECTION - B
1. Are you aware from reliance mutual funds?
a) Yes b) No
2) In this highly volatile market, do you think mutual funds are destination for investment?
a) Yes b) No
3)
Are you satisfied with the different types of products
and services provided
by the reliance mutual funds?
a) Yes b) No
4) While investing your money, which factor you prefer most? Anyone
a) Liquidity b) Low risk
c) High return d) Company reputation
5) Have you ever invested in mutual funds?
a) Yes b) No
6) If yes, in which type of funds of mutual funds you want to invest?
a) Tax saver funds b) Index funds
c) Sectorial funds d) gold funds
7) Which investment do you feel more profitable?
a) Fixed deposit b) Mutual funds
c) Equities d) Other
8)
Which are the primary
sources of your knowledge about mutual funds
as an investment option?
Corresponding to your choice how would you rate their influence on your final
mutual funds purchase decisions? 1 is the lowest and 5 is the
highest rating.
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
Television |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Newspaper |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Friends |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
10) How do you rate the risk associated with mutual funds?
a) Low d) Moderate
c) High
11) When you invest in mutual funds which mode of investment will you prefer?
a) One time investment
b) Systematic investment plan
12) In which mutual funds you have invested?
a) SBIMF
b) UTI
c) RELIANCE
d) HDFC
e) KOTAK
f) ICICI
g) JM MUTUAL FUNDS
h) Other
Click here to download the office file

















![Himachal Pradesh - General Knowledge (H.P.-GK) Important multiple choice questions [MCQ] Series-G [PDF]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEihP5ys_xY1amJSiIEX-cY2NLnL0-9UBNpv2MTUAeFLcs2pnfZKTYrt7Qd-n_r7M4evoPfvEdhHqdfZJOZSq9KYkrGcH_xqghVowGepqKTjk95dgtUVABcsuzhRcsWto5IrCi3jfZcRgnUztoalEsVLXewOeyf2k3keJIRTSQvEIfkRVVhFXlOSAxAK/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/Untitled.png)
![Himachal Pradesh - General Knowledge (H.P.-GK) Important multiple choice questions [MCQ] Series-E [PDF]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgvoEofOEWgV2ZbKnHN0TIymi5Ri4OkMlEtZSBr-uBeGEIfoHH7VbEK_Znb2bog2mo5eWSYvhgC3VT2gUixmn_it7TP13EVdxDKI21dEHngzbUbjy0myZ6X86bS6IaqkkweK-uwRYQdW3GLNFQtUkWJhmffquskJFEii-4T0hAtUzte3rXwegACr8hy/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/Series%20E.JPG.webp)
![Himachal Pradesh - General Knowledge (H.P.-GK) Important multiple choice questions [MCQ] Series-D [PDF]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg9VldQ-XZ0MMTk4_GjvWCEGKlUs3CVQAFbyqJbBsylLvzF6tGZHY18wjUAv-1ZhFh1jKWDtDfVzFOqUTbvjxs6eHM0ctieIeuxPJadN77BsFpuHkHqlkx_O47iDIZaxCQzXMptimaiWmiYXvqeDrg94tRV9KFRIkVOtS_kd05hZpC8xjp70CoTaG8R/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/Series%20D.JPG.webp)


0 Comments